Underground storage are one of the most if not the most effective way to drastically reduce evaporation by completely eliminating several factors such as wind, sun and air.
The main advantage of this method is that the loss of valuable land area is completely avoided.
However, the disadvantage of this method is that it requires high capital cost due to the size and engineering of the infrastructure used for the storage.
This can be diminished by storing the water in the aquifer. But by doing so, water needs to be pumped for use, which entails additional pumping costs and large energy consumption.
Deep Dam Design
Less water will evaporate if the ratio of the surface area to the volume is reduced.
The surface area can be minimised by building the dam as deep and as narrow as is practical.
This is highly effective but can be costly if the dam is already constructed.
The presence of a saline underground water table limits the depth to which a dam can be dug.
Another strategy is to construct the dam into cells so that independent areas of water can be managed to minimise surface areas.
For example, divide a dam into two or more equal sized cells of water.
Then, draw water from the first cell and, when possible, transfer the balance to the other cell(s) thus reducing the surface area of the remaining volume.
Windbreaks
Wind breaks involve planting trees or other plants that act as wind breakers, thus reducing the movement of air over the water surface
This greatly reduces evaporation
Trees can also provide some shade which will further reduce evaporation.
However, wind breaks can only be employed on small water bodies.
On big dams, the wind break effect is limited to a short distance from the rim of the reservoir, leaving the inner water exposed.
Aquatain
Aquatain is a silicone based liquid that is spread in a very thin layer on top of bodies of water to form a barrier stopping contact between water and air – and therefore reducing the amount of loss to evaporation.T
The maker, Guyco, claims Aquatain will reduce evaporation by more than 50%
Waterguard
WaterGuard is a unique liquid which spreads over the surface of water to form a very thin film and reduce evaporation.
WaterGuard is produced from
polymers which repel each other very strongly when they come in contact with the water.
This results in a strong spreading action across the surface, forming a liquid ‘blanket’ to reduce evaporation.
Water losses from evaporation are immense.
A single square metre of water surface can easily lose up to 8 litres to evaporation every day in summer, and a one hectare dam can lose up to 80,000 litres – water that is essential for animals and growing crops.
Trials in the US have achieved evaporation savings of 50% and above.
Vegetable oil
This is also the principle behind using a floating liquid such as vegetable oil
A thin layer of vegetable oil will float to the surface and prevent water molecules from making contact with the air – thereby reducing evaporation
However, in many circumstances, it is not appropriate to use oil.
The problem with this method is that the wind can break the vegetable oil up & blow it to shore
Chemical WER
Chemical WER (fatty alchohol) forms a thin film that has been found to be effective for reducing evaporation
Some studies cite a 46% reduction
Chemical WER is also fairly safe to the environment as it is biodegrable and permeable to oxygen
However, wind velocities and temperature does affect Chemical WER, and it is generally not used when winds exceed 10-15 km/h – or when the temperatures exceed 40-42C.
Chemical WER is also expensive to purchase and apply – and it is only a short term measure.
Dam plants
You can add free-floating water plants, such as water lilies and duckweed, in quantities that block approximately 40 to 60 percent of the dam’s water surface.
The floating plants’ flowers and foliage help to shade the dam effectively to keep it cool and reduce sun exposure, and in turn minimise the risk of algae blooms and weed invasions.
Choose plants that grow below the surface of the water.
Submerged plants have the largest contribution to water quality.
They function as oxygenators during daylight hours, providing oxygen for fish, and they supply fish with excellent cover.
Water lillies are an excellent solution
They reduce surface temperature & the area exposed to wind
The growing of dam reeds would have same effect – although greatly impeding flow of water
Depth Segmentation
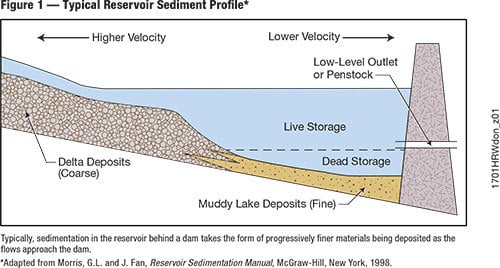
Reducing the exposed water surface works best if some shallow portions in the reservoirs can be easily separated from the rest of the lake.
The method consists in building dykes to isolate the shallow portion of the reservoir and divert the water to deeper area – and is somewhat effective in drought prone areas.
Evaporation losses are eliminated in those sections, thus reducing the evaporation losses over the entire reservoir.
Unfortunately, it is dependent on the reservoir topography, and can be somewhat costly to implement.
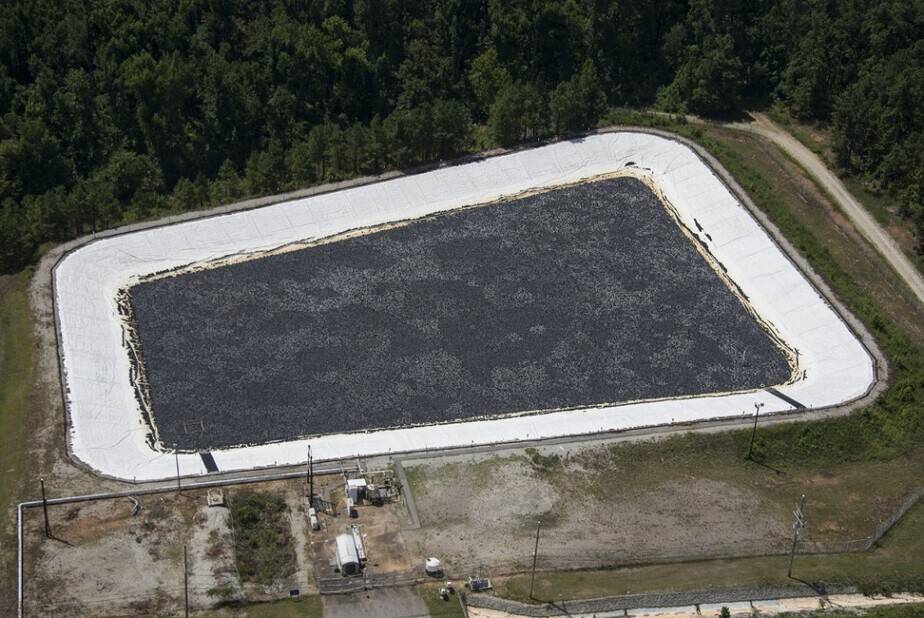
Dam covers
Floating cover systems were first introduced over 60 years ago.
Many advancements in design and materials have been made over the years.
Some of the newer materials includes hypalon, polypropylene, PVC, HDPE, LLDPE, geotextile, XR-5 and XR-3
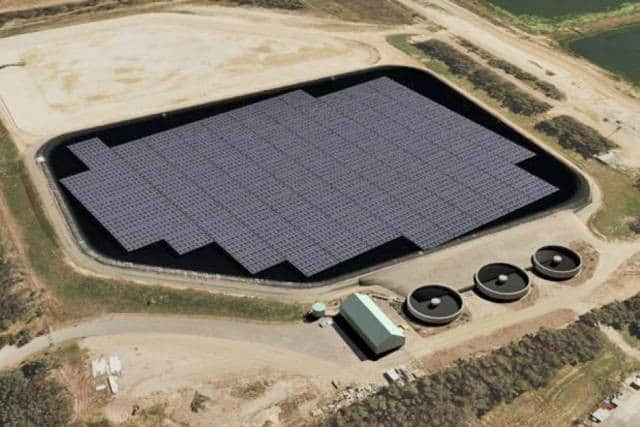
Despite having a higher capital cost than wind breaks, complete reservoir covers offer the best cost /efficiency ratio out of all the existing methods to effectively reduce evaporation.
While quite as not effective as enclosed underground storage (99+% reduction in evaporation losses), some modular floating covers are getting very close (98%)
These covers are very similar to those used in swimming pools.
The downside of this method is cost.
To cover a dam of 4.5 Ha, the cost would be approximately $250,000 – or about $5.55 a square metre.
Assessment criteria for dam covers
When considering dam covers, there are a number of questions that have to be weighed up:
- How stable will the cover be in high winds?
- How long will it last?
- Will it be stable when the dam is dry?
- Will it leach toxic substances into the water?
- How will it stand up to what is a corrosive environment – continual contact with water and air and some level of salinity; exposure to ultra-violet light that can degrade some plastics?
- Some products are easily and cheaply installed by the land owner, others require expensive installation by specialists.
- What warranty is there – and is the company likely to be around in five years if you need to call on the warranty?
- Does the product need to cover only the water, or does it need to be large enough to allow for anchoring beyond the lip of your dam – making a big impact on the final price?
- If your dam wall is vegetated? How much damage will be done to this during installation?
- Many of the products on the market are flammable. The probability of a bushfire during the life of the cover must be considerable; in some areas more than others.
Dam cover drawbacks
Despite progress in material and manufacturing process, geomembrane and solid covers in general still present several drawbacks:
- Can not use this method if you have fish in your dam
- Geomembrane can tear, resulting in expensive repairs costs.
- High maintenance cost
- They must be custom designed to match the exact shape of the dam or reservoir.
- They are affected by rain, ice, frost and snow.
- They cannot be installed on full ponds.
- Insurance cost associated with those type of covers are high.
- They block access to the liquid.
- Limited warranty: 5-10 years.
- Overtime, vegetation growth appears on top of the cover.
- Install requires specialised equipment and trained crew.
- Cannot be easily reused or transferred to a different liquid containment.
- Are not easily compatible with certain type of surface aerators.
- Price becomes substantially higher for long lasting, thick, heavy duty geomembrane.
Below are some of the products that fall into the category of modular floating dam covers
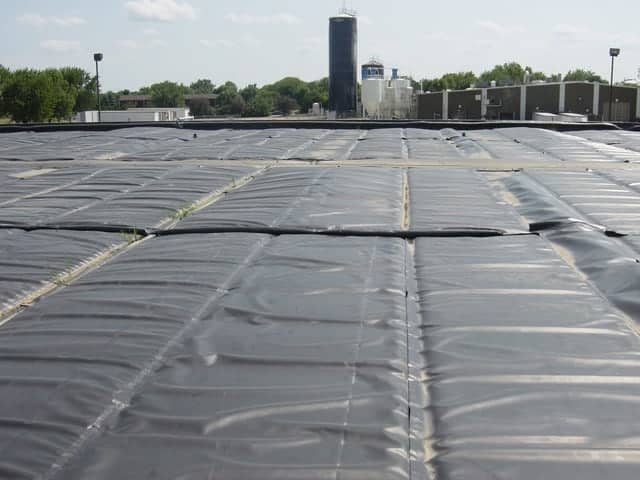
E-Vap Cap
E-Vap Cap is a floating polyethylene sheet cover
The floating cover consists of a unique, multi-layered, polyethylene membrane 540 microns in thickness that contains its own buoyancy cells.
It carries a 5-year pro-rata warranty against UV breakdown due to sunlight exposure (independent NATA laboratory testing indicates a much longer “life” expectancy than 10 years).
Optional thicker material, up to 1000 microns is available giving greater warranty and a design life of 20 years
For a dam measuring 20m x 30m, the quantity of material required – including allowances for top of banks, anchor trenches, welding overlaps – would be approx. 1011.84sqm
This would indicate an approximate price of $10,175 – or $20 per sqm
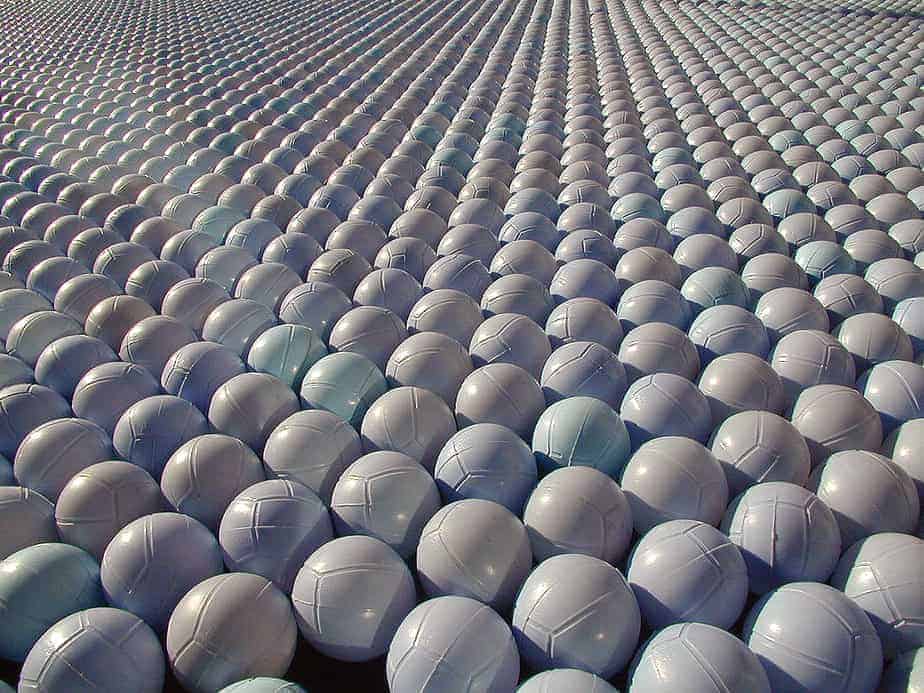
Evap-Mat
Evap-Mat is a product of DeVere Mining Technology Limited
Evap-Mat is comprised of laminated 20 micron, stainless steel mesh and 0.4mm bubble HDPE sheet.
The cover is anchored to the storage floor by cables attached to a buried polyethylene pipe.
It is designed to only cover 90% of the water surface area.
Evap-Mat is easy to install, heat reflective and self-protecting in high winds (up to 150 kph) whether empty or full.
The cover is also suitable for all storage sizes, shapes and profiles up to 2 km wide.
It is claimed that Evap-Mat may reduce evaporation by up to 90 per cent -depending on the water level of the storage.
Costs: $3.50/m2 for complete installation.
Life expectancy is 30 years.
Resistant to UV light and oxidation.
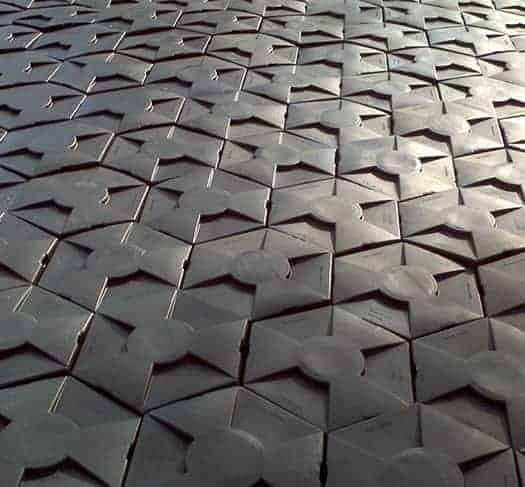
Hex Dome
Hex Dome is an independent modular system made from UV resistant recycled plastic – with a life expectancy of 25 years
Each module covers one square metre – and it has been shown to greatly reduce the effects of wave action
Hex Dome claims to reduce evaporation by up to 90%
Costs: the anticipated cost is $4.50-8.00/m2
Quit Evap
Quit Evap is a rectangular modular floating cover, manufactured from 0.5-0.75 mm thick polypropylene sheet with polystyrene floats.
The modules are interconnected by Velcro straps.
The full scale modules are up to 5 m x 25-30 m.
Quit Evap can cover 90-95 per cent of the water surface and reduce evaporation by 85-90 per cent.
Durability:
The cover has a minimum life span of 5 years with a potential life of 8-10 years – the cover is also UV stabilised.
Costs: the estimated cost is around $6.00-8.00/m2 plus transport and installation.
Raftex